The paper "Determination of thermal conductivity of asphalt paving mixtures using finite element method" (Volume 243, May 2020, 118250) published by the research group of Academician Fwa Tien Fang of the Highway School of Chang'an University in the Journal of Construction and Building Materials was well-known in the global engineering field. Advances in Engineering (AIE) was selected as a key scientific article, and a special report was made on November 13, 2020. Dr. Longjia Chu of the College of Highway of Chang'an University is the first author of the paper, Academician Fwa Tien Fang is the corresponding author, and PhD student He Lei is the co-author.

Screenshot of AIE website special report
Advances in Engineering (AIE) was established in Canada in 2005. Its main purpose is to report important scientific research results and innovative technologies in the engineering field in a timely and rapid manner. Papers reported by AIE need to have special scientific importance. After rigorous selection by the international committee of experts, AIE will select outstanding papers with important scientific and technological contributions around the world for special reports. The directions include general engineering, chemical engineering, electronics, machinery, civil engineering, nanotechnology, materials, biomedical engineering, and selected papers. The conditions are harsh, and the selection rate is less than 1‰ of the total number of papers published in all engineering fields mentioned above. AIE has a broad readership, with a monthly audience of up to 850,000 scientific researchers, used to track the latest breakthrough technological developments in the world.
General idea and technical process of research on thermal conductivity of asphalt mixture
Asphalt mixture is a viscoelastic material with temperature sensitivity. When studying the thermal properties of asphalt concrete, the thermal conductivity k is an important input parameter. The laboratory determination of the thermal conductivity of the mixture requires professional equipment and is time-consuming and labor-intensive.
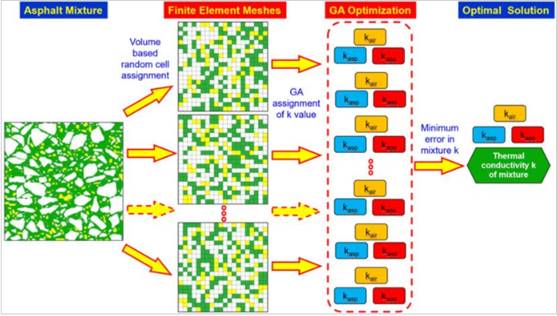
Since 2017, the team of academician Fwa Tien Fang of the College of Highway of Chang'an University has proposed a computer program to determine the thermal conductivity of asphalt mixtures through numerical simulations for the disadvantages of measuring the thermal conductivity of the mixture in the laboratory. k. This method first expresses the asphalt mixture as a two-dimensional (or three-dimensional) row-column structure of unit thickness, and randomly allocates the number of units occupied by each component according to the volume ratio of each component in the mixture. Then, based on the random row-column structure, a thermal conductivity simulation model of the asphalt mixture is established, and the thermal conductivity k of the mixture is calculated using the thermal conductivity theory. When the k value of asphalt binder and aggregate is unknown, the model is calibrated through genetic algorithm to obtain the required k value. After being calibrated, the model can determine the thermal conductivity k of the asphalt mixture under different porosity, and no experiment is needed to determine it.
The calculation method of the research team can quickly obtain the thermal conductivity k of the mixture, which greatly reduces the time and effort required for the design of the mixture ratio; in addition, the porosity of the asphalt mixture will continue to decrease under the action of traffic load, thereby affecting the mixture The thermal conductivity k of the material, the calculation method proposed by the research team can quickly obtain the changing law of k, and it can also be used to calculate the temperature field of the asphalt mixture during the construction of the intelligent roller compactor on the road surface.
Advances in Engineering report link:
https://advanceseng.com/thermal-conductivity-mixtures-without-laboratory-testing/



